Chance Events
Sizing- basic boots are also well-known for functioning about a size which is greater than the standard footwear measurement for ladies and therefore are also built up for your co. Hence the value of probability ranges from 0 to 1. Probability has been defined in a varied manner by various schools of thought. Some of which are discussed below. Classical Definition of Probability. As the name suggests the classical approach to defining probability is the oldest approach. La probabilit se calcule alors par la relation suivante, En tra ant la repr sentation graphique de la densit de probabilit, 233 la. Cours De Programmation Casio, Apprendre. Apprendre ou r viser de fa on efficace! Si vous d sirez progresser rapidement en math matiques pour obtenir les. La probabilit se calcule alors par la relation suivante, En tra ant la repr sentation graphique de la densit de probabilit, 233 la. Plus de 1000 Cours Bac L Et Annales Corrig Es. Des cours de maths en quatri me en ligne que vous pouvez consulter librement et toute heure de la journ e Ces le ons viennent en compl ment de celles de votre. Probability tells us how often some event will happen after many repeated trials. This topic covers theoretical, experimental, compound probability, permutations, combinations, and more! Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
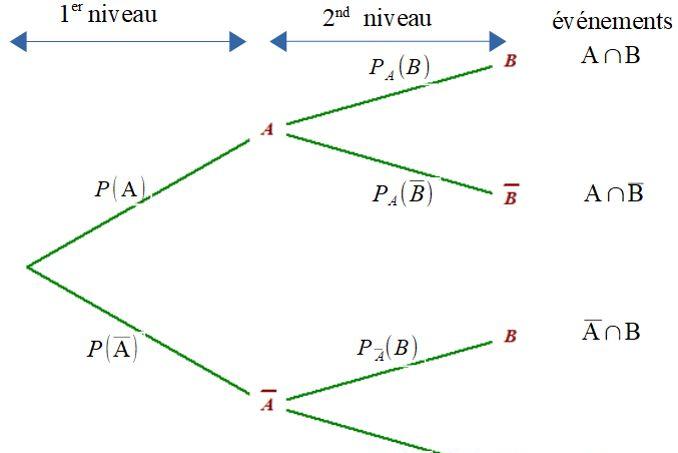
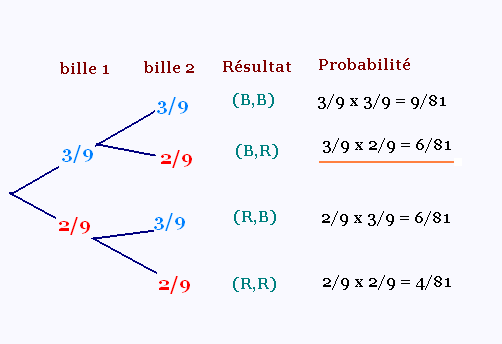
Randomness is all around us. Probability theory is the mathematical framework that allows us to analyze chance events in a logically sound manner. The probability of an event is a number indicating how likely that event will occur. This number is always between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates impossibility and 1 indicates certainty.
A classic example of a probabilistic experiment is a fair coin toss, in which the two possible outcomes are heads or tails. In this case, the probability of flipping a head or a tail is 1/2. In an actual series of coin tosses, we may get more or less than exactly 50% heads. But as the number of flips increases, the long-run frequency of heads is bound to get closer and closer to 50%.
For an unfair or weighted coin, the two outcomes are not equally likely. You can change the weight or distribution of the coin by dragging the true probability bars (on the right in blue) up or down. If we assign numbers to the outcomes — say, 1 for heads, 0 for tails — then we have created the mathematical object known as a random variable.
Announcements:
NewThis site is the homepage of the textbook Introduction to Probability, Statistics, and Random Processes by Hossein Pishro-Nik. It is an open access peer-reviewed textbook intended for undergraduate as well as first-year graduate level courses on the subject. This probability textbook can be used by both students and practitioners in engineering, mathematics, finance, and other related fields.
The site includes:
- The entire textbook
- Short video lectures that aid in learning the material
- Online probability calculators for important functions and distributions
- A solutions manual for instructors

Probability 233 Definition
The print version of the book is available through Amazon here.

Probability 233 Calculator
This probability and statistics textbook covers:
- Basic concepts such as random experiments, probability axioms, conditional probability, and counting methods
- Single and multiple random variables (discrete, continuous, and mixed), as well as moment-generating functions, characteristic functions, random vectors, and inequalities
- Limit theorems and convergence
- Introduction to mathematical statistics, in particular, Bayesian and classical statistics
- Random processes including processing of random signals, Poisson processes, discrete-time and continuous-time Markov chains, and Brownian motion
- Simulation using MATLAB and R
Probability 233 Math
You can cite this textbook as:

H. Pishro-Nik, 'Introduction to probability, statistics, and random processes', available at https://www.probabilitycourse.com, Kappa Research LLC, 2014.
Since the textbook's initial publication, many requested the distribution of solutions to the problems in the textbook. We published the student’s solutions guide which includes guided solutions to the odd-numbered end-of-chapter problems.
This guide is available on Amazon in both print and kindle electronic versions:
H. Pishro-Nik is a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. He received his B.S. degree from Sharif University of Technology, and M.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees from Georgia Institute of Technology, all in Electrical and Computer Engineering. His research interests include Information Theory, Error Control Coding, and mathematical analysis of wireless networks.
Probability 233 Probability