
Carotid arterial stenting (CAS) is a minimally invasive endovascular interventional procedure that can potentially offer the same advantage as surgery (carotid endarterectomy).

ACAS and ACST could show a minor preventive effect of carotid surgery in carotid stenosis between 60% and 99%. A refined assessment of risk according to stenosis grade could not be made because of various methodological problems. In ACAS, absolute risk reduction of stroke and/or death was 5.9% and in ACST 5.4%, in a time frame of 5 years. CarotidArteryStenosis Executive Committee for the Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study Objective. P=m- To determine whetherthe addition of carotid endarterectomy to. What ACAS authors failed to emphasize is that screening truly asymptomatic patients with noninvasive tests, performing carotid angiography on all patients with positive tests, and finally performing carotid endarterectomy on patients with greater than 60% stenosis of any internal carotid artery will never prevent strokes in the long run.
Acas Carotid Trial
Indications

Indications for carotid stenting are evolving with endarterectomy trials that evaluate the carotid stenosis cutoff values for treatment. Currently, the indications include:
- symptomatic patients with ≥70% stenosis (NASCET trial)
- asymptomatic patients with >60% stenosis (ACAS study)
- symptomatic patients with stenosis of at least 50-69% stenosis
- carotid artery dissection or pseudoaneurysm
Contraindications
Acas Carotid
- complete carotid occlusion
- major disabling stroke on the ipsilateral side/disabling dementia
- intracranial tumor/hemorrhage
- unstable plaque or thick calcification at the site of carotid stenosis
- extreme tortuosity of the vessel
Complications
Acas Criteria Carotid Stenosis
- preprocedural cerebrovascular accident (~8%) 3
- recurrent carotid arterial stenosis or in-stent restenosis (~6% at 1 year) 4
- hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid artery stenting (1-2%): headache, seizures and intracranial hemorrhage 6
Acas Carotid
Alternative treatment options
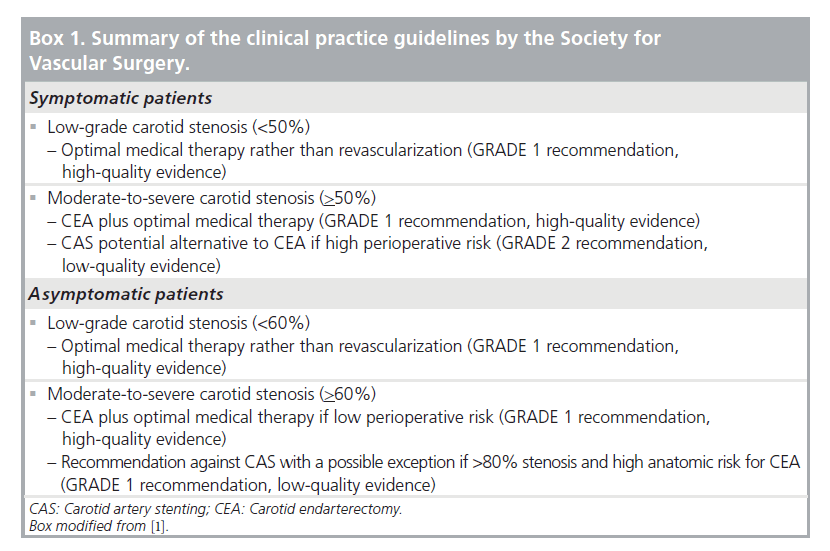
Outcomes
Operator skills and experience have a profound impact on patient outcomes following CAS. One systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature found Carotid Endarectomy (CEA) to be superior to CAS in freedom from stroke/death within 30 days of treatment, with the incidence of stroke/death within 30 days of treatment was 4.7% for CAS and 3.5% for CEA 8.
History and etymology
- the first percutaneous transluminal carotid angioplasty (PTA) was performed by Charles Kerber in 1980 5.
- somewhat surprisingly the word 'stent' is actually an eponym, originally named after Charles Stent (1807-1885), a largely-forgotten British dentist. He invented an improved material for forming dental impressions and set up a company to manufacture it. During the Great War, J F Esser, a Dutch surgeon used a mold of Stent's Compound as a fixative for skin grafting in injured infantrymen. This innovative use was rapidly adopted into practice, and stenting as a concept rapidly segued into multiple specialties 7.
Acas Trial Carotid
- 1. Baerlocher MO, Stewart B, Asch MR et-al. Performance of carotid stenting, vertebroplasty, and EVAR: how many are we doing and why are we not doing more? A survey by the Canadian Interventional Radiology Association. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2008;59 (1): 22-9. - Pubmed citation
- 2. Sacks D, Connors JJ. Carotid stent placement, stroke prevention, and training. Radiology. 2005;234 (1): 49-52. doi:10.1148/radiol.2341041628 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Pelz D, Andersson T, Soderman M et-al. Advances in interventional neuroradiology 2005. Stroke. 2006;37 (2): 309-11. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000201436.30248.ec - Pubmed citation
- 4. Gröschel K, Riecker A, Schulz JB et-al. Systematic review of early recurrent stenosis after carotid angioplasty and stenting. Stroke. 2005;36 (2): 367-73. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000152357.82843.9f - Pubmed citation
- 5. Liistro F, Di Mario C. Carotid artery stenting. Heart. 2003;89 (8): 944-8. doi:10.1136/heart.89.8.944 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 6. Karapanayiotides T, Meuli R, Devuyst G et-al. Postcarotid endarterectomy hyperperfusion or reperfusion syndrome. Stroke. 2004;36 (1): 21-6. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000149946.86087.e5 - Pubmed citation
- 7. Stenting. (2001) Surgical Endoscopy. 15 (4): 423. doi:10.1007/s004640080116 - Pubmed
- 8. Zhang L et. al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Carotid Artery Stenting Versus Endarterectomy for Carotid Stenosis: A Chronological and Worldwide Study. (2015) Medicine. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001060 - Pubmed